TOKYO KEIKI RAIL TECHNO INC.
|
|
[Ultrasonic Rail Inspection Car 'URIC']
 The
ultrasonic rail inspection car's flaw detection system detects
internal rail flaws as the car runs along the rail and with the
distance measurement system option can provide accurate detection
of flaw position. The
ultrasonic rail inspection car's flaw detection system detects
internal rail flaws as the car runs along the rail and with the
distance measurement system option can provide accurate detection
of flaw position.
In addition to flaw detection, additional system
options include sectional wear measurement utilizing the newest
in image processing
technology and rail corrugation measurement using lasers.
The ultrasonic
rail inspection car has established an enviable record of shipments
to the Japan Railways companies including
the Shinkansen as well as every major private railway company.
<Features>
- Capable of high-speed ultrasonic rail inspection (40km/h).
- Manual calibration of position based on kilometer post references
for distance information. In addition, accuracy can be enhanced
using the "DataDepot" System (option) which detects
position data automatically.
- Flaw data is presented in "B" scope color display
in real time. Also display recognition provides results of defect
type, classification and position data. Store and playback functions
are also provided which enable evaluation and discrimination
of natural defects and artificial "defects" such as
bolt holes, etc., which results in increased reliability of test
data. "A" scope display in real time is also available.
<Delivery milestones>
| 1965 |
Tokaido-Shinkansen (formerly Japan National Railway) |
| 1976 |
Sanyo-Shinkansen (formerly Japan National Railway) |
| 1983 |
Tohoku-Shinkansen (formerly Japan National Railway) |
| 1988 |
Tokyu Corporation |
| 1989 |
Central Japan Railway (Shinkansen) |
| 1990 |
Seibu Railway |
| 1992 |
West Japan Railway |
| 1996 |
East Japan Railway (Shinkansen) |
| 1997 |
Tobu Railway |
| 1999 |
West Japan Railway (Shinkansen)
Kyushu Railway |
| 2001 |
Keihin Electric Express Railway |
| 2003 |
Kinki Nippon Railway
Odakyu Electric Railway |
| 2004 |
Kyushu Railway (Shinkansen)
East Japan Railway
Seibu Railway |
| 2005 |
Hokkaido Railway |
| 2006 |
Central Japan Railway (Shinkansen) |
| 2008 |
Tokyu Corporation |
| 2009 |
West Japan Railway (Conventional Line No.2) |
|
[Switch profile gauge 'SPG-3']
 'SPG-3S'
(standard gauge model) 'SPG-3S'
(standard gauge model)
'SPG-3N' (narrow gauge model)
The Switch Profile Gauge is a new system for automated turnout
inspection and maintenance.
The system adopts the light slice method
using a laser slit light source and two-dimensional CCD cameras.
The system simultaneously
measures the information necessary for calculating the wearing
depth of rails and crossings, back gauges, flangeway widths,
and track geometry. The system automates conventional manual
track
inspections and produces databases of measurement data which
incorporates office automation technology in the maintenance
and management
task.
|
<Features>
-
Light weight and user friendly operation
This device is pushed through a turnout manually. The data collection device is an easily transportable system that is making it light enough for two workers to carry, assemble and mount or dismount.
|
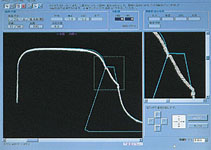
Sample display of wearing depth at tongue rail |
- Speedy measurement
Measurement times are 10 to 15 minutes per turnout since the system can simultaneously
measure the wearing depth of the rail and geometry of the track within
the turnout.
- Simultaneous measurement
The four parameters (gauge, longitudinal level, alignment and cross level)
pertaining to track irregularity can be measured simultaneously with respect
to the siding. Image data can be displayed on the screen in order to allow
visual confirmation of the wear depth of the rail.
- High precision measurement
|
| >> List of our services |